The Essential Role of Industrial Model Makers in Architecture
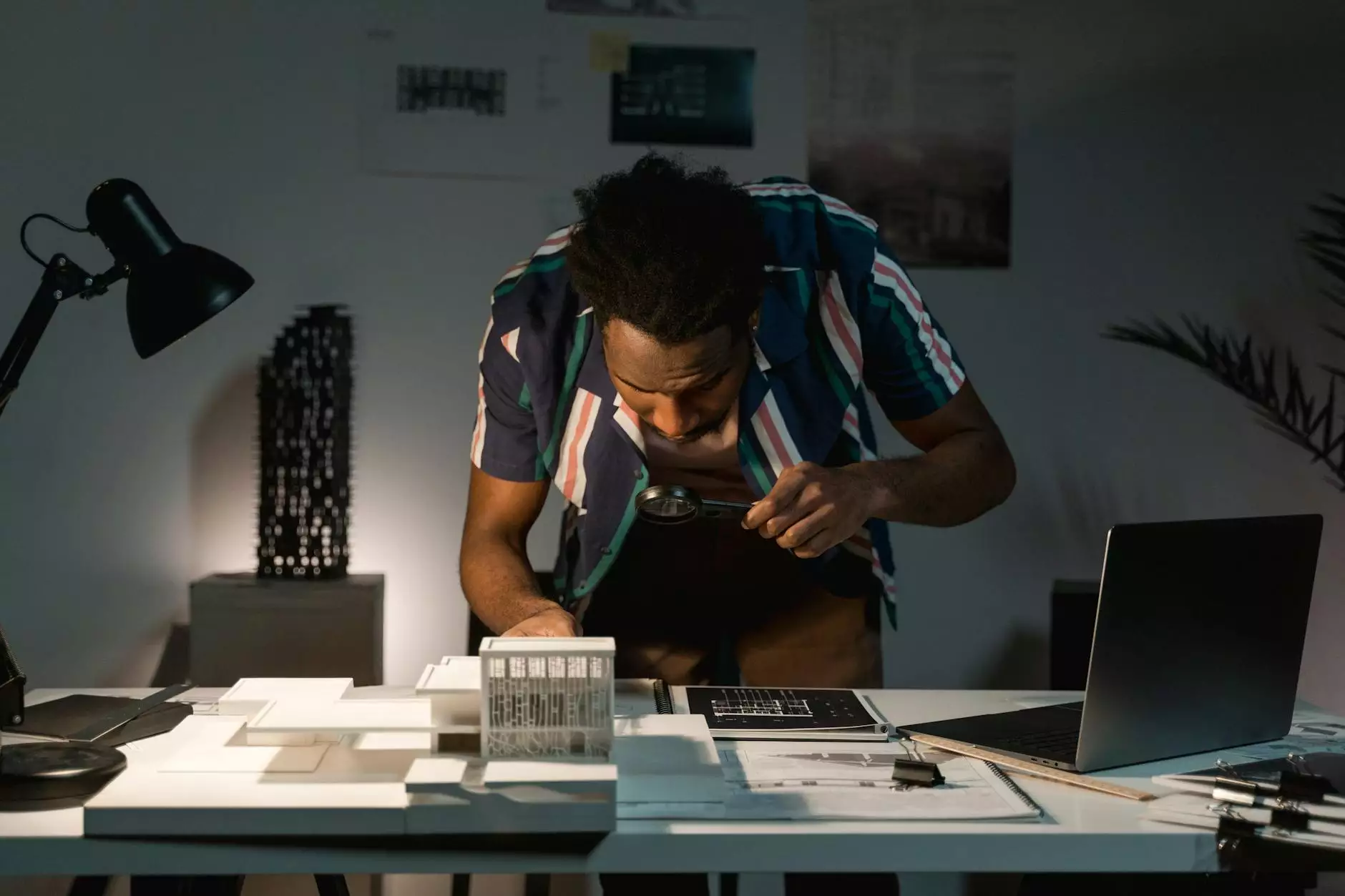

In the realm of architecture, the contribution of industrial model makers is often underestimated. These highly skilled artisans play a crucial role in the design and development of architectural projects, bridging the gap between conceptual ideas and tangible structures. This article delves deep into the world of industrial model making, exploring its significance, processes, and the benefits it brings to architects and their clients.
Understanding Industrial Model Making
Industrial model making is the art and science of creating tangible representations of products, structures, or environments. It is a specialized practice that employs various techniques, materials, and technologies to bring architectural visions to life. The models produced can range from small-scale concepts to large, intricate presentations that encapsulate the entire project.
The Importance of Models in Architecture
Architectural models serve multiple purposes, making the role of industrial model makers invaluable:
- Visualization: Models provide a visual understanding of a project that sketches and digital renderings often cannot convey. They allow stakeholders to appreciate the scale, proportions, and aesthetics of a design.
- Communication: A physical model facilitates better communication among architects, engineers, clients, and investors. It acts as a common reference point for discussions, ensuring that everyone shares a coherent understanding of the project.
- Evaluation and Analysis: Models enable architects to evaluate design choices and spatial relationships. By physically interacting with a model, architects can identify potential issues and make necessary adjustments before construction begins.
- Marketing and Presentation: High-quality architectural models can be powerful marketing tools. They help convey the vision to potential buyers, investors, or regulatory bodies, often making a persuasive case for the project.
Key Skills and Techniques of Industrial Model Makers
To create effective models, industrial model makers employ a diverse set of skills and techniques:
Materials Selection
The choice of materials is paramount in model making. Common materials include:
- Plexiglass: Known for its clarity and strength, commonly used in architectural models to create glass-like features.
- Wood: Offers a natural aesthetic and can be shaped easily to demonstrate unique design elements.
- Foam Board: Lightweight and easy to cut, ideal for creating detailed, layered models quickly.
- 3D Printing Materials: With advancements in technology, 3D printing has become a preferred method for producing intricate designs with high precision.
Techniques of Model Construction
Model makers utilize several techniques to construct accurate and detailed models:
- Hand Crafting: This traditional technique involves manually cutting, shaping, and assembling materials, allowing for a high degree of customization.
- Digital Fabrication: Employing technologies like laser cutting and CNC machining, digital fabrication allows for precise cuts and complex designs that would be difficult to achieve by hand.
- 3D Printing: A revolutionary method that enables the production of complex geometries directly from digital models, providing rapid prototyping and constructive flexibility.
Steps in the Industrial Model Making Process
The process of creating an architectural model involves several key stages:
1. Concept Development
The first step is understanding the architect’s vision. This involves discussions to ascertain the required scale, level of detail, and specific features to be included in the model.
2. Design Planning
Once the concept is clear, the model maker develops a plan. This includes sketches and digital visuals to outline how the model will be structured and what materials will be used.
3. Material Preparation
With a plan in hand, the model maker gathers and prepares the necessary materials. This may involve cutting sheets of wood, molding plastic, or loading filaments for a 3D printer.
4. Model Construction
This is the most labor-intensive stage where the actual assembly takes place. The model maker meticulously crafts each component, ensuring accuracy and attention to detail.
5. Finishing Touches
After assembly, the model undergoes finishing processes such as painting, texturing, and adding realistic elements like landscaping or figures to enhance visual appeal.
6. Presentation
Finally, the model is presented to the architect and their clients. This step may involve explaining the design and addressing any queries, ensuring everyone is aligned on the project’s vision.
Benefits of Collaborating with an Industrial Model Maker
Partnering with a skilled industrial model maker offers numerous advantages for architects:
- Enhanced Creativity: Working with a model maker can inspire architects to think differently about their designs, pushing the boundaries of creativity.
- Increased Efficiency: Models can reveal design flaws early in the process, saving time and resources in the long run.
- Improved Client Satisfaction: A well-crafted model often leads to positive client feedback, fostering trust and enhancing relationships.
Conclusion: The Future of Industrial Model Making in Architecture
As the architectural landscape continues to evolve with advances in technology and design principles, the role of industrial model makers becomes increasingly vital. Their ability to create tangible representations not only aids in visualization and communication but also serves as a creative catalyst for innovation. As architects and clients alike recognize the value of well-crafted models, the demand for skilled industrial model makers is sure to grow, cementing their place in the future of architectural design.
For architects looking to elevate their presentations and designs, collaborating with a professional industrial model maker can make all the difference. Embrace the future of architecture with models that inspire, inform, and ignite creativity.